Patent on the Fourth Dimension
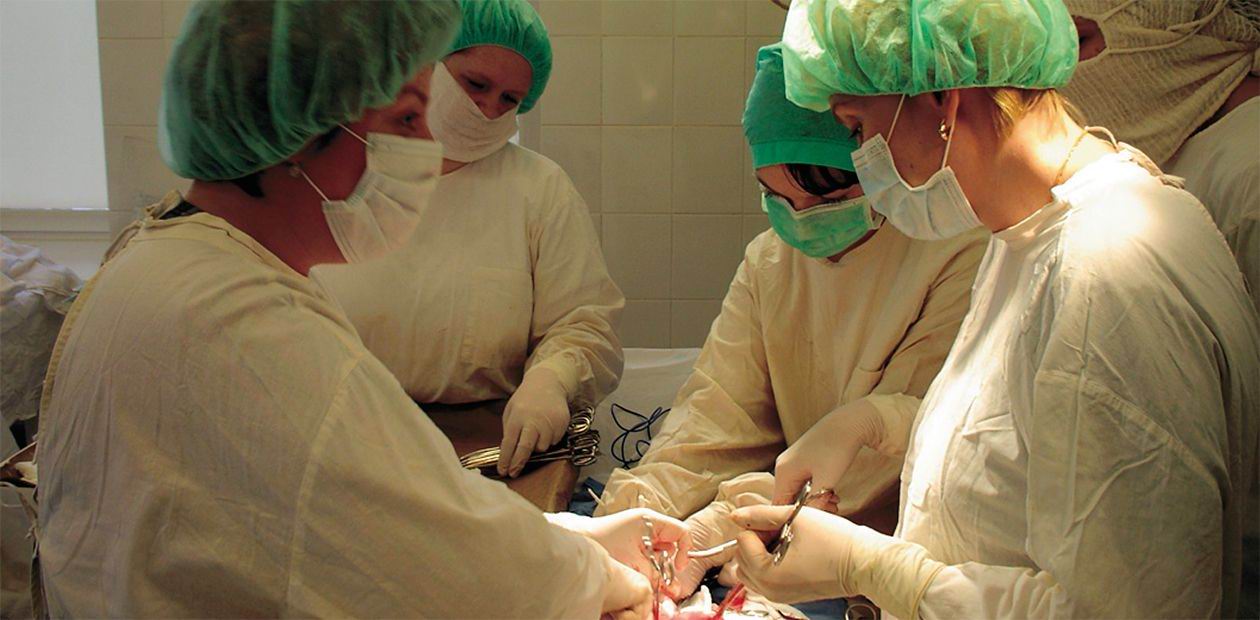
At the Novosibirsk Center for New Medical Technologies, Institute of Chemical Biology and Fundamental Medicine, Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, a new method has been developed - 4D contrast histerosonography - intended to diagnose changes in myometrium (uterus muscle), including endometriosis - the most widespread and enigmatic gynecological disease. The essence of the method is that ultrasonic study of the uterus is conducted after it is filled with a contrast substance, which makes direct symptoms of endometriosis visible. Having filled the uterus cavity as much as possible, the hyperechogenic contrast substance penetrates endometriotic ducts and contacts with their content. As a result, the ducts are contrasted and the monitor shows a specific picture, which reminds of a snow-covered tree.
Doctors call endometriosis a civilization malady as the reason for its prevalence is low birth rate. Women pregnant or breast-feeding during most of their reproductive age are immune to the disease.
In principle, it is sort of a benignant tumor: cells of the uterus (endometrium) proliferate in the areas outside the uterine cavity. As a rule (in 70—90 % cases), the process localizes in the uterus wall and involves development of grandular and stromal elements in the muscular wall of the uterus (myometrium). The symptoms of endometriosis are pain, hemorrhage resulting in an inflammation in the surrounding tissues, and increase in the size of the uterus. Further development of this disease often becomes the reason for infertility. According to the World Health Organization, genital endometriosis is considered an independent factor of infertility with 9—15 % women.
Diagnostics of endometriosis poses a serious problem for modern medicine because the existing ultrasonic and other investigations do not give a clear picture of the uterus corpus condition. Ultrasonic studies show fibroids and endometriosis cysts; however, these manifestations of the disease are characteristic of by no means all patients.
Endometriosis is traditionally diagnosed based on a collection of indirect symptoms, neither of which is the absolute proof for the presence of the disease. The clinical picture provided by ultrasonic studies (for example, inner endometriosis of the uterus) may disagree with laparoscopy results (e. g., outer endometriosis, often in a more developed stage).
The only reliable evidence is histological analysis, which requires excision of a small (or sometimes rather large) part of the uterus muscle. This “gold standard” technique is applied only in emergencies because this rather crippling operation is undesirable for women of reproductive age planning to have children.
No methods for corpus visualization have existed until recently, when the so-called 4D contrast histerosonography was developed at the Novosibirsk Center for New Medical Technologies, Institute of Chemical Biology and Fundamental Medicine SB RAS. The essence of the method is that ultrasonic study of the uterus is conducted after it is filled with a contrast substance, which makes direct symptoms of endometriosis visible. Having filled the uterus cavity as much as possible, the hyperechogenic contrast substance penetrates endometriotic ducts and contacts with their content. As a result, the ducts are contrasted and the monitor shows a specific picture, which reminds of a snow-covered tree.
Why is it called 4D? The study of the uterus is three-dimensional, which allows to estimate more exactly the affected area, and the forth dimension is time. The diagnosis is made not after a medical examination following the study of the snapshot but in real time, like an ordinary ultrasound investigation. The patient does not need any additional preparation.
In fact, any ultrasound investigation is two-dimensional as an organ is seen on a planar surface. In the course of investigation, the doctor chooses the direction in which to move about this surface so as to see the necessary details as clearly as possible. The new equipment allows computer processing of a wide range of scanned images of an area selected and constructing a 3D model based on them; however, it does not give a full picture of the organ in real time.
In our case, thanks to the gradual filling of the uterus with a preliminary estimated volume of the contrast substance, the doctor can see in real time whether there are any endometrioid ducts (thin channels). The presence of the latter provides for a highly reliable diagnosis of endometriosis, except the cases when the channels are not directly connected to the uterus body. Without revealing these ducts endometriosis can be confused with a myoma, a benignant tumor also resulting in an increase of the uterus size. However, if a growing myoma is treated surgically, endometrioses can be cured conservatively using hormones.
Introduction of the new method has allowed the doctors of the Center for New Medical Technologies, Institute of Chemical Biology and Fundamental Medicine SB RAS, to detect endometriosis in over 3,000 patients. The contrast substance consists of water and oxygen, which rules out any potential allergies. Of great importance is an accurate estimate of the maximum volume of the liquid, which is necessary for the substance to fill the endometriosis ducts.
Yet another application of the method deserves a special mention. This is evaluation of the thickness of cicatrices on the uterus left after cesareans, abortions, and other operations involving dissection of the uterine cavity. Such diagnostics is vitally important because any gynecological operation such as inserting an IUD, diagnostic curettage or abortion may cause ruptures of thinned out cicatrices. As a result, the uterus may have to be removed.
Evaluation of the cicatrix thickness is of diagnostic value to women who are planning a pregnancy: “good” cicatrices will allow the uterus to stretch to the necessary size as the embryo grows. Conventional ultrasound investigation of the cicatrix thickness makes accuracy up to 1 millimeter impossible whereas a 1 or 2 millimeter error is crucial: a cicatrix thinner than 4 mm is a serious threat against maintenance of pregnancy.
The method of 4D contrast histerosonography has been developed by a team of doctors working for the Novosibirsk Center for New Medical Technologies, Institute of Chemical Biology and Fundamental Medicine SB RAS, and for one of them became the subject of the candidate thesis. A joint patent has been obtained for the technique of the 4D endometriosis test.
The editors thank the doctors of the Novosibirsk Center for New Medical Technologies Candidates of Medicine S. A. Kurganov and A. A. Makhotin for their assistance with preparation of this publication